Unveiling the Miracle of lactıon: Nourishing Infants, Fostering Bonds

Introduction to Lactıon
Lactıon, the process of producing breast milk to feed infants, stands as a fundamental pillar in early childhood development.
It not only provides optimal nutrition but also imparts immunological protection, cognitive benefits, and the invaluable chance to form a strong maternal bond.
This comprehensive guide aims to delve into the intricate world of lactation, exploring its mechanisms, benefits, challenges, and solutions.
Understanding the Process of lactıon
Lactıon is initiated by hormonal changes during pregnancy and childbirth. Prolactin and oxytocin levels rise, stimulating milk production and facilitating its release to the infant.
This nutrient-dense milk, often referred to as “liquid gold,” provides complete sustenance for newborns and infants up to six months old.
The World Health Organization recommends exclusive breastfeeding for the first six months, followed by continued partial breastfeeding up to two years.
The Nutritional Powerhouse of Breastmilk

Breastmilk, often hailed as “liquid gold,” boasts an unparalleled nutritional profile. It contains a perfect blend of macronutrients and micronutrients, adapting its composition to meet the changing needs of a growing baby.
The complexity and variation of breast milk surpass any formula, making it nature’s ideal source of nourishment.
Macronutrients:
- Carbohydrates (lactose) for energy
- Proteins (whey and casein) for tissue development
- Fats (essential fatty acids) for brain growth
Micronutrients:
- Vitamins (A, B, C, D, E, K)
- Minerals (calcium, iron, zinc, magnesium)
- Antioxidants (selenium, taurine)
Immunological Benefits of Colostrum and Mature Milk
Colostrum, the initial breast milk produced during and after birth, is rich in immunoglobulins, lactoferrin, leukocytes, and antimicrobial compounds.
These components supplement a newborn’s undeveloped immune system. Mature breast milk continues to bolster immunity through oligosaccharides, lysozyme, lactoferrin, and immunoglobulins, reducing the risk of various infections and diseases.
Impact of Breastfeeding on Brain Development
Breastmilk plays a pivotal role in influencing brain growth and cognitive function. Components like DHA, choline, and taurine contribute to neural development.
Long-term studies suggest that exclusively breastfed infants for six months or more exhibit higher IQs, better memory, and improved problem-solving abilities.
The Maternal Bond and Breastfeeding
Beyond physical health, breastfeeding fosters a deep maternal bond through skin-to-skin contact and the release of oxytocin, known as the “love hormone.”
Extended breastfeeding has been linked to enhanced mutual gaze, affection, and bonding, contributing to socioemotional health.
Common Challenges and Solutions for Successful Breastfeeding
While lactation is a natural process, it can present challenges. Common hurdles like latching issues, low milk supply, nipple pain, and pumping concerns have practical solutions.
Seeking guidance from lactation consultants, support groups, and online resources can help overcome these challenges.
Benefits of Lactıon for Women
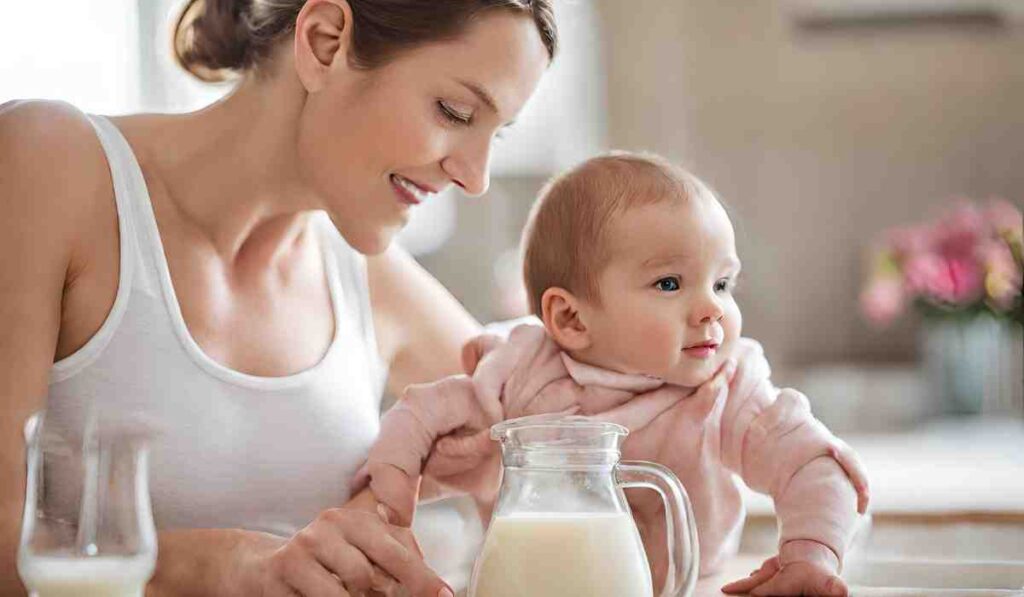

Breastfeeding offers numerous advantages for mothers, including bonding with the baby, health benefits, a natural contraceptive effect, cost-effectiveness, convenience, customized nutrition, reduced allergy risk, eco-friendliness, postpartum uterine health, and enhanced emotional well-being.
Conclusion
In conclusion, lactıon is a remarkable evolutionary gift that ensures babies receive the best start in life.
The nutritional richness, immunological strength, cognitive enhancement, and maternal bonding facilitated by breastmilk make breastfeeding the ideal choice.
Despite challenges, education, support, and determination pave the way for successful lactation, promoting both short and long-term well-being for mothers and infants.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Lactation:
Q1: What is lactation?
A: Lactation is the process of producing and secreting breast milk from the mammary glands to nourish an infant.
Q2: When does lactıon begin?
A: Lactıon typically begins during pregnancy, but milk production increases significantly after childbirth.
Q3: How can I increase my milk supply?
A: To boost milk production, ensure proper hydration, frequent breastfeeding, a balanced diet, and adequate rest.
Q4: Is breastfeeding painful?
A: While some discomfort is common in the early stages, breastfeeding should not be painful. Seek help from a lactation consultant if you experience pain.
Q5: How often should I breastfeed my baby?
A: Newborns often feed every 2-3 hours, and as they grow, the time between feedings may extend.
Q6: Can I breastfeed if I return to work?
A: Yes, many working mothers successfully breastfeed by pumping and storing breast milk for their infants.
Q7: What foods should I avoid while breastfeeding?
A: Avoid excessive caffeine, alcohol, and certain medications. Consult with a healthcare provider for guidance.
By embracing lactation, mothers provide their babies with a gift that nurtures health, strengthens bonds, and fosters lifelong well-being.
Additional FAQs
Q8: What role does Lactıon play in the emotional well-being of both mothers and infants?
A8: Lactıon fosters emotional well-being by triggering the release of oxytocin, the “love hormone,” promoting a sense of calmness, security, and motherly love.
This empathetic response strengthens the maternal bond and contributes to the socioemotional health of both mother and baby.
Q9: Can Lactıon impact the taste of breast milk, and how does it evolve over time?
A9: Yes, Lactıon influences the taste of breast milk. Initially, colostrum has a distinct taste, and as lactation progresses, breast milk adapts to the flavors of the mother’s diet.
This exposure to diverse tastes may contribute to an infant’s acceptance of a variety of foods during weaning.
Q10: How does Lactıon contribute to postpartum uterine health?
A10: Lactıon triggers the release of oxytocin, which helps the uterus contract. This contraction reduces postpartum bleeding and aids in uterine recovery, contributing to the overall health and well-being of the mother after childbirth.
Q11: Can Lactıon be affected by stress, and how can mothers manage stress during breastfeeding?
A11: Yes, stress can impact Lactıon. High stress levels may interfere with milk letdown.
Mothers can manage stress through relaxation techniques, seeking support from loved ones, and creating a calming environment during breastfeeding.
If persistent, consulting with a healthcare professional or lactation consultant is advisable.
Q12: Is Lactıon only beneficial for the first few months, or does it continue to provide advantages as the baby grows?
A12: Lactıon continues to offer benefits as the baby grows. While the composition of breast milk adjusts to meet changing nutritional needs, the emotional bonding, immune support, and cognitive advantages persist throughout the breastfeeding journey, extending well beyond the first few months.
Q13: How can mothers maintain a balance between Lactıon and their professional life?
A13: Balancing Lactıon and professional life involves strategic planning. Working mothers can schedule pumping sessions, ensure proper milk storage, and communicate their breastfeeding needs with employers.
Creating a supportive work environment and utilizing breastfeeding-friendly policies contribute to a successful balance.
Q14: Are there specific foods that can enhance Lactıon and improve the quality of breast milk?
A14: While there’s no magic food that guarantees increased Lactıon, certain foods like oatmeal, fenugreek, and fennel are believed to support milk production.
However, maintaining a well-balanced diet, staying hydrated, and following individual nutritional needs are key factors in supporting Lactıon.
Q15: Can Lactıon impact the sleep patterns of infants?
A15: Yes, Lactıon can influence infant sleep patterns. Breast milk contains components like tryptophan and melatonin, which may contribute to a calming effect.
However, individual variations exist, and establishing a consistent bedtime routine is crucial for promoting healthy sleep habits in infants.




















































































































































![[noblocc] Kicked For Being AFK](https://everytalkin.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/noblocc-Kicked-For-Being-AFK-Strategies-in-Online-Gaming-1024x597.jpg)